Water conservation is key for those who care about the environment. A rainwater collection system is a smart way to cut down on water use. It helps you live more sustainably by changing how your home uses water. By using a rainwater harvesting system, you can make a big difference.
Even small catchment systems can hold 40 to 100 gallons. This is enough for most homes. You can use rainwater for things like watering plants and cleaning outside, which saves municipal water.
Rainwater collection is versatile and useful. It’s great for watering plants and cleaning up outside. A good rainwater system is good for the planet and your home.
Key Takeaways
- Rainwater collection systems offer an eco-friendly water management solution
- Storage capacities range from 40 to 100 gallons for typical residential setups
- Systems can be retrofitted to existing structures with relative ease
- Reduces reliance on municipal water supplies
- Supports sustainable home water conservation efforts
Understanding Rainwater Harvesting Fundamentals
Rainwater collection turns rainfall into a valuable resource. It involves capturing, storing, and using rainwater for various needs.
Rainwater harvesting is more than just collecting water. It’s a smart choice for those who care about the environment and want to save water.
What Makes Rainwater Collection Effective
Several factors make rainwater collection effective:
- Catchment Area Efficiency: A 1,000 square foot rooftop can collect about 600 gallons in one rain event
- Precise surface design and slope for optimal water capture
- Strategic placement of collection systems
- Understanding local precipitation patterns
Key Terms and Concepts
Learn important terms in rainwater harvesting:
- First Flush Diverter: Removes initial contaminated water runoff
- Conveyance System: Gutters and downspouts that direct water
- Storage Solution: Tanks designed for water preservation
The Science Behind Water Collection
“Rainwater harvesting transforms a natural resource into a sustainable water management solution.”
The science of rainwater collection is based on simple math. For example, 1 inch of rainfall over 1,000 square feet gives about 623 gallons of water.
Key scientific principles include:
- Rainfall volume calculation
- Surface area optimization
- Water quality assessment
- Filtration and purification techniques
By understanding these basics, homeowners can create effective rainwater systems. These systems help collect and conserve water efficiently.
Benefits of Installing a Rainwater Collection System
Rainwater harvesting is a key part of sustainable water management in homes. The market for it is growing, valued at $890.2 million. Homeowners see the big advantages of using these systems.
The benefits of rainwater harvesting go beyond saving water. Here are some key advantages:
- Economic Savings: It can cut down on monthly water bills
- Environmental Protection: It helps reduce stormwater runoff and pollution
- Energy Efficiency: It uses gravity, not pumps, saving energy
- Property Value Enhancement: It makes homes more eco-friendly
Practical benefits of rainwater collection are many. Homeowners can cut down on their use of municipal water. A single downspout can collect 300 to 600 gallons of rainwater. This is a big help for many household needs.
Rainwater harvesting also helps the environment. It supports many environmental goals. By collecting rainwater, communities can:
- Reduce greenhouse gas emissions
- Minimize soil erosion
- Support local aquatic ecosystems
- Decrease strain on water management systems
Innovative homeowners see rainwater harvesting as more than a trend. It’s a sustainable way to manage water. It offers real benefits for both homes and the environment.
Essential Components of a Rainwater Harvesting System
To set up a DIY rainwater system, you need to know the main parts. These parts work together to collect and store water. A good design turns your roof and area into a water collection system.
Catchment Areas and Roofing Materials
The catchment area is the start of your water collection plan. The type of roof you have affects how well it collects water:
- Metal roofs: Collects water best (90% efficiency)
- Clay tiles: Great for filtering water
- Asphalt shingles: Collects water fairly well
For a 1,000 square foot roof, you can get about 623 gallons of water per inch of rain. The roof material is key to water quality.
Gutters and Downspouts
Good gutter design is vital for a rainwater system. Here are some tips:
- Make sure gutters slope ¼ inch per 10 feet
- Use gutter guards to cut down on upkeep by 50%
- Install first flush diverters to skip the dirty water
Storage Tanks and Cisterns
Choosing the right storage is key for your DIY system. You can pick from 50 to 10,000 gallon tanks, based on your needs:
- Polyethylene tanks: Light and resistant to corrosion
- Fiberglass tanks: Strong and easy to fix
- Stainless steel tanks: Very durable but cost more
Tip: Pick dark tanks to stop algae and keep them 10-18 inches from your house.
Setting Up a Rainwater Collection System
Setting up a rainwater harvesting system needs careful planning. It’s about turning your property into a water-saving powerhouse. Knowing the basic steps is key.
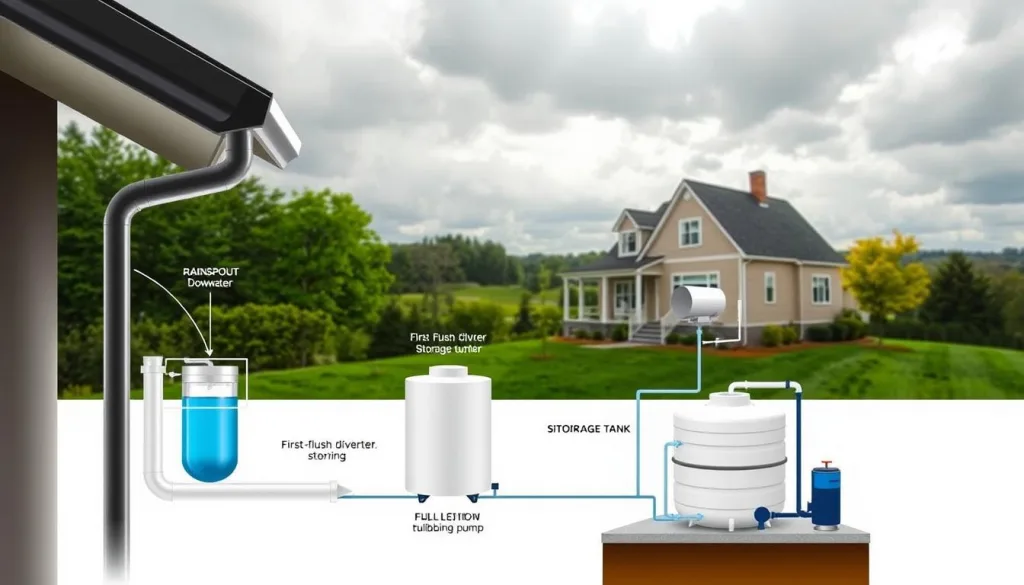
The first step is to figure out how much water you can collect. This depends on a few important things:
- Roof size
- Local rainfall
- How well the system collects water
Here’s a simple fact: 1 inch of rain on a 1,000 square foot roof can give you about 623 gallons of water. This shows how much rainwater harvesting can help save water at home.
When designing your system, think about these parts:
- The roof as the water collector
- Gutters and downspouts
- A first flush diverter
- A storage tank
- A way to filter the water
There are many storage options, from small rain barrels to big underground tanks. The best one for you depends on your needs, the weather, and how much space you have.
Pro tip: Check local laws and tax breaks before setting up your rainwater system.
Places like Texas, Arizona, and California really support rainwater harvesting. It’s becoming more popular among eco-friendly homeowners.
Choosing the Right Storage Solutions
Finding the best storage solution is key in installing a rainwater tank. Your system’s design depends on several factors. These factors affect how well and efficiently it works.
There are many types of rainwater storage systems. Each has its own benefits. Knowing these options helps homeowners choose the right water collection method.
Above-Ground vs. Underground Tanks
When designing your rainwater system, you face two main choices:
- Above-Ground Tanks
- Easier to install
- Less expensive upfront
- Easy to access for maintenance
- Underground Tanks
- Less visible
- Keeps water at a steady temperature
- Protects from the environment
Material Considerations
| Material | Durability | Cost Range | Maintenance |
|---|---|---|---|
| Polyethylene | High | $500-$2,000 | Low |
| Concrete | Very High | $1,500-$5,000 | Medium |
| Fiberglass | High | $1,000-$3,500 | Low |
Size and Capacity Planning
Choosing the right tank size is important. It depends on several factors:
- Local rainfall patterns
- Roof area
- How much water you use
- Space available
A typical home can collect about 0.623 gallons per square foot of roof area for each inch of rainfall. By looking at your specific needs, you can create an efficient system. This system will collect more water and use less from the city.
Water Quality and Filtration Methods
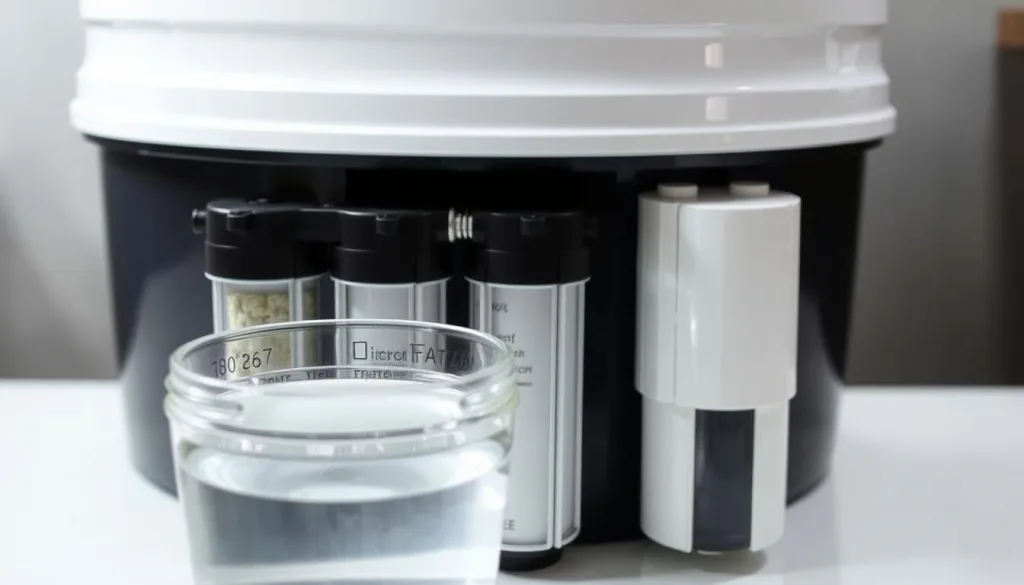

Having clean water is key in any rainwater harvesting system. Rainwater is a green water source, but it needs proper filtration for safe use. Knowing how to collect rainwater well helps homeowners create a good water treatment plan.
Rainwater can have many contaminants that need careful handling. These include:
- Sediment and debris
- Bacteria and viruses
- Chemical pollutants
- Atmospheric particulates
Good filtration methods are vital to make rainwater safe to use. Different filters tackle different types of contaminants:
| Filtration Method | Effectiveness | Best Used For |
|---|---|---|
| Sediment Filters | Remove large particles | Initial debris elimination |
| UV Sterilization | 99% bacteria removal | Microbial decontamination |
| Activated Carbon | Chemical compound reduction | Improving taste and odor |
| Reverse Osmosis | 99% impurity removal | Potable water preparation |
For drinking water, a multi-stage filtration system is best. Daily water quality testing is a must when using rainwater for drinking. It’s important to remove at least 99% of particles bigger than 3.0 microns.
Setting up a strong rainwater harvesting system needs careful thought on filters, regular upkeep, and constant quality checks. By doing these things, homeowners can make rainwater a safe, green water source.
Maintenance and System Care Guidelines
Keeping your rainwater collection system in good shape is key for its long-term performance and water quality. Rainwater system maintenance tips help you keep your investment safe and boost water collection.
For your system to last, you need to care for it regularly and act fast when needed. This ensures it works well for years to come.
Seasonal Maintenance Tasks
Seasonal care is essential for your rainwater system:
- Clean gutters and downspouts every two months
- Inspect mesh filters for debris and blockages
- Check storage tanks for algae or sediment
- Flush the system to remove contaminants
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Be ready to fix common problems in your rainwater system:
- Algae Growth: Tanks in sunlight can get yellow. Regular checks stop big problems.
- Filter Maintenance: Clean first-flush diverters and mesh filters for better water quality
- Sediment Control: Flush the system often to remove particles
By sticking to these maintenance tips, you’ll have a reliable water collection system. It supports sustainable living and saves on your water bill.
Legal Considerations and Permits
Setting up a rainwater collection system can be tricky. It’s important to know the local laws. Most states in the U.S. support rainwater harvesting.
Different states have different rules for rainwater harvesting:
- 43 out of 48 states either have no restrictions or actively promote rainwater collection
- Only 5 states have substantial regulations on rainwater harvesting
- Specific state requirements can differ significantly
Before you start, take these legal steps:
- Check local municipal regulations
- Verify permit requirements
- Review possible incentive programs
- Confirm allowable water usage
Pro tip: Contact your local planning department to get precise information about rainwater collection regulations in your specific area.
Some states offer great incentives for rainwater harvesting. Texas gives tax breaks, and Arizona requires it for some commercial buildings. In 2022, Arizona started a grant program for home rainwater systems.
Rainwater harvesting is legal in all 50 U.S. states, with most permitting non-potable outdoor applications for residential properties.
Remember, rules change based on how you plan to use the water. Using it for irrigation is usually easier than for indoor use. Always check local laws to make sure your system is okay.
Cost Analysis and Return on Investment
Setting up a rainwater collection system needs careful financial planning. The cost starts at $1,000 to $5,000 for most homes. This depends on the system’s size and complexity.
Here are the main costs for a typical rainwater harvesting setup:
| System Component | Cost Range |
|---|---|
| Storage Tank (Polyethylene) | $2,000 – $4,000 |
| Installation Labor | $50 – $100 per hour |
| Gutters and Downspouts | $900 – $5,000 |
| Filtration System | $75 – $200 |
Rainwater harvesting offers more than just water savings. Homeowners gain long-term financial benefits:
- Lower municipal water bills
- Potential tax credits and rebates
- Less money spent on watering landscapes
“Investing in a rainwater collection system is not just an environmental choice, but a smart financial strategy for modern homeowners.”
Your investment will pay off in 3-5 years. This depends on local water costs and how much you use the system. Places with high water rates and lots of rain will see quicker returns.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability Benefits
Rainwater harvesting systems are a key to environmental sustainability. They help homeowners cut down their ecological footprint and support water conservation.
The benefits of rainwater harvesting go beyond saving water. Here are the main impacts:
- Reduction of stormwater runoff by up to 50%
- Decreased water pollution in local waterways
- Mitigation of soil erosion risks
- Decreased energy consumption in water treatment processes
Water conservation is more important than ever due to climate change. Rainwater harvesting systems offer a sustainable option for communities facing environmental changes.
“Every drop of harvested rainwater is a step towards environmental preservation” – Water Conservation Expert
Here are some amazing facts about rainwater harvesting:
| Environmental Benefit | Impact Percentage |
|---|---|
| Stormwater Runoff Reduction | 45-55% |
| Energy Savings in Water Treatment | 30-40% |
| Greenhouse Gas Emission Reduction | 25-35% |
Even big cities are starting to use rainwater harvesting. The O2 Arena in London collects rainwater from a huge 90,000 m² area. This shows how these systems can work on a large scale.
By choosing rainwater harvesting, people join a global effort for sustainable water management. This helps protect local ecosystems and the world’s water resources.
Conclusion
Setting up a rainwater collection system is a big step towards saving water and caring for the environment. By 2004, over 100,000 homes in the US had already started using these systems. The benefits of rainwater harvesting go beyond just saving water.
By using a rainwater collection system, homeowners can cut down on their water bills and help the planet. The average home uses about 90,000 gallons of water each year. These systems can be tailored to fit your area’s rainfall, from 30 inches to 160 inches a year.
Starting a rainwater collection system might seem hard, but the benefits are worth it. They can lower your water costs and give you a backup water source when it’s dry. With over half of US states facing dry spells by July 2022, having an alternative water source is more important than ever.
I urge you to see rainwater harvesting as more than just a home project. It’s a way to help save water and support sustainable living. By doing this, you’re not only improving your home but also helping the planet.
FAQ
How much rainwater can I collect from my roof?
Are rainwater collection systems legal everywhere?
Is collected rainwater safe to drink?
How much does a typical rainwater collection system cost?
What maintenance does a rainwater collection system require?
Can I use rainwater for my entire household?
What materials work best for rainwater storage tanks?
How do I prevent algae growth in my rainwater tank?
Source Links
- 6 Tips for Installing a Rainwater Collection System – https://learn.eartheasy.com/articles/tips-for-installing-a-rainwater-collection-system/
- Rainwater Harvesting 101 | Your How-To Collect Rainwater Guide – https://www.watercache.com/education/rainwater-harvesting-101?srsltid=AfmBOor_VXTqHlzmR295TPPgSaF9BRZq99SzXfuY0ka1DpJyxpGF62mf
- Rainwater Harvesting 101 | Your How-To Collect Rainwater Guide – https://www.watercache.com/education/rainwater-harvesting-101?srsltid=AfmBOooDiyxrqa6l74awt_g6lNSdMKwYmvUKxyuPO71eOmRWiEytjkRW
- Rainwater Harvesting 101 – https://rainwatermanagement.com/blogs/news/rainwater-harvesting?srsltid=AfmBOopGp7umtPtiKi43QNnb62YORMi0w7qnqk7gHzhFyCuEtgb_fyU8
- Rainwater Harvesting System: Steps, Advantages & Types – https://www.ultratechcement.com/for-homebuilders/home-building-explained-single/descriptive-articles/the-steps-to-an-efficient-rainwater-harvesting-system
- The Benefits of Rainwater Harvesting – https://rainwatermanagement.com/blogs/news/benefits-of-rainwater-harvesting?srsltid=AfmBOoqDDp5XZjtCDmK8uUi3dCF5NyQzBiIfkqqWcPn8K7sCeKIqyhJ9
- The Many Benefits and Advantages of Rainwater Harvesting – https://www.watercache.com/faqs/rainwater-harvesting-benefits?srsltid=AfmBOoq_xzRn2NaEZq_edJ0gwchSR_f08zewiZR991xWm2f8MvCYy5vC
- Beginner’s Guide to Rainwater Collection (With Top 7 Benefits) – https://www.familyhandyman.com/article/beginners-guide-to-rainwater-collection-with-top-7-benefits/?srsltid=AfmBOoordNsLGOhBXoIWWj2-KrSdwltacjK2kXokJ2AB8n_DygfGXzrd
- PDF – https://extension.arizona.edu/sites/extension.arizona.edu/files/pubs/az1565.pdf
- Rain Tanks | Components of a Successful Rainwater Harvesting System – https://www.ntotank.com/blog/components-of-a-successful-rainwater-harvesting-system?srsltid=AfmBOoqahwimc04Iim6BDrhA3INAlQoqMsm1iOGhHiHzdzg4-00xcfn4
- The Components of a Rainwater Harvesting System – https://rainwatermanagement.com/blogs/news/components-of-rainwater-harvesting-system?srsltid=AfmBOoqMtNufhdYhEupWse84wRRbrRzHdrZDwVk_r6JGmEdhJJsaWMQP
- Rainwater Harvesting 101 | Your How-To Collect Rainwater Guide – https://www.watercache.com/education/rainwater-harvesting-101?srsltid=AfmBOop63cLUwPQwl1nidrLjeBtWvrJfbk50_XYgidqb7vwNLcj7GM5b
- Rain Tanks | How to Design a Rainwater Harvesting System – https://www.ntotank.com/blog/how-to-design-a-rainwater-harvesting-system?srsltid=AfmBOoptQqAuLBFBqMIb7R299dn1R_O2RFJ8Rv2P6Q_nonQff86HOUqD
- A Beginner’s Guide to Rainwater Harvesting – https://www.treehugger.com/beginners-guide-to-rainwater-harvesting-5089884
- Rainwater Storage Options – New – https://rainwatermanagement.com/pages/rainwater-storage-options?srsltid=AfmBOoomK_7nzW-A16BebLrcNclNmetTLk1TD1MsoxfHP_o6USgQRC_g
- Rainwater Harvesting 101 | Your How-To Collect Rainwater Guide – https://www.watercache.com/education/rainwater-harvesting-101?srsltid=AfmBOoqOvw-oKEd8JPyrrSVb44aaMfj0ibOxCTsxfXd8fKz6PdSRQomY
- What should I consider before installing a Rainwater Harvesting System? – Innovative Water Solutions LLC – https://www.watercache.com/faqs/what-should-i-consider-before-installing-a-rainwater-harvesting-system?srsltid=AfmBOorzlAk2n1XOJJxhZ3rJK4seTz55jOS21jq9ClC3PWbOuXmuvBkf
- Rainwater Harvesting Systems Technology Review – https://www.energy.gov/femp/rainwater-harvesting-systems-technology-review
- How to Collect Rainwater for Drinking – https://www.freshwatersystems.com/blogs/blog/how-to-collect-rainwater-for-drinking?srsltid=AfmBOorODEJCCBA_kTvIbqtgS7xnj1hczjYiEuic2lGHYY4JciwbdYT0
- Best Practice For Maintaining RWH – https://www.rainyfilters.com/about-us/blogs/best-practice-for-maintaining-rwh
- Rainwater Harvesting 101 – https://rainwatermanagement.com/blogs/news/rainwater-harvesting?srsltid=AfmBOoouq1_rgmiAa1231f7O5LLkXU6yKjoQN_v9Tmbs78pRvvBdJo_9
- How to Set Up a Rainwater Harvesting System: A Simple Guide – Tips and How To – https://spicymoustache.com/how-to-set-up-a-rainwater-harvesting-system-a-simple-guide/
- Rainwater Harvesting 101 | Your How-To Collect Rainwater Guide – https://www.watercache.com/education/rainwater-harvesting-101?srsltid=AfmBOoom9Z7dBM2KMSXsrsctNPQ9IC-pr0cxfIMFp-5hm3q5yQucErxQ
- Rainwater Harvesting Laws You Need to Know About (2023) – https://4perfectwater.com/blog/rainwater-harvesting-laws
- Rainwater Harvesting Laws, Regulations, and Rights by US State – https://www.ntotank.com/blog/rainwater-harvesting-laws-regulations-and-rights-by-us-state?srsltid=AfmBOoo8vNGas7gqWOrw1895Y0R5UbdNIoKe2kcpTiO-YmdKiTnjVqv6
- Rainwater Collection System Cost | Cost to Install Rainwater Harvesting System | Fixr – https://www.fixr.com/costs/rainwater-collection-system
- Microsoft Word – Final BHicks Rainwater Harvesting MP 04-23-08.doc – https://dukespace.lib.duke.edu/bitstreams/7ca6b735-b4fe-4095-ab25-c3ab52fe0322/download
- The environmental impact of rainwater harvesting and using water tanks at home – https://smartwateronline.com/news/the-environmental-impact-of-rainwater-harvesting-and-using-water-tanks-at-home?srsltid=AfmBOopjb3hgwfr5367d2eCv0J7Va5d9utV-tTwo0xZ1TmfaALrMKogA
- Rainwater Harvesting: A Sustainable Approach to Water Management – https://medium.com/mark-and-focus/rainwater-harvesting-a-sustainable-approach-to-water-management-4903b219b8b4
- Design of Rainwater Harvesting Systems in Oklahoma – Oklahoma State University – https://extension.okstate.edu/fact-sheets/design-of-rainwater-harvesting-systems-in-oklahoma.html
- Rainwater Cisterns: Design, Construction, and Treatment – https://extension.psu.edu/rainwater-cisterns-design-construction-and-treatment
- Harvesting Rainwater for Residential Water Security – https://learn.eartheasy.com/articles/harvesting-rainwater-for-residential-water-security/


